Recording them at historical cost could misrepresent their worth to stakeholders, especially investors who rely on real-time data. GAAP and IFRS permit or require mark-to-market accounting for these assets to ensure financial statements reflect current economic conditions. However, comparability can be limited when market conditions change significantly.
205-11 Depreciation.
A consistent application of the cost principle would establish meaningful comparisons of financial statements from period to period, thus laying bare the trends that reflect actual performance. Auditors prefer historical costs; they cost principle accounting definition are based on documents and free of subjective adjustments for enhanced audit accuracy and ease in audit procedures. The cost principle would allow meaningful comparisons of financial statements period by period, thus laying bare the trends that reflect actual performance. Accounting principles explain how transactions, such as sales, purchases, and payments, should be reported. Before accounting principles were introduced, companies were free to record and report financial data as they saw fit. This made financial statements harder to compare and made it far easier for companies to skew their numbers positively.

Operating Costs
Since the closing of the acquisition, Infosys has struggled with this deal. Many allegations were thrown around about the deal, which has hampered these companies’ profiles because the fair value was reduced significantly. Boost your confidence and master accounting skills effortlessly with CFI’s expert-led courses! Choose CFI for unparalleled industry expertise and hands-on learning that prepares you for real-world success. When you access this website or use any https://weatherfordtransportation.com/bookkeeping-9/self-employed-quickbooks-worth-the-cost/ of our mobile applications we may automatically collect information such as standard details and identifiers for statistics or marketing purposes. You can consent to processing for these purposes configuring your preferences below.
Scenario 1: A Manufacturing Company’s Machinery
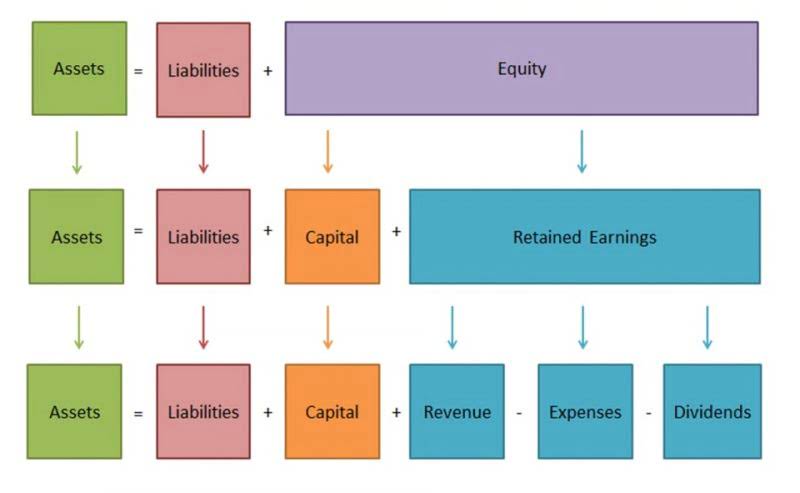
Cost principles are essential rules or guidelines that govern how costs should be measured, allocated, and reported in financial statements, contracts, and pricing strategies. They provide clarity and consistency, ensuring that costs are appropriately recognized and reported according to legal, regulatory, and contractual standards. Whether in business operations, government contracting, or financial accounting, following cost principles helps ensure transparency, accuracy, and compliance, minimizing risks and enhancing the decision-making process. Cost principles refer to Suspense Account a set of guidelines or rules that determine how costs should be measured, allocated, and accounted for in financial reporting, budgeting, and pricing. These principles are designed to ensure that costs are recorded accurately and consistently, reflecting the true economic expense of producing goods or services.

205-22 Lobbying and political activity costs.
- As per Cost Principle in the book of Google, the value of YouTube will be shown as $1.65 billion.
- For example, a company that buys a building for $500,000 will record it at that amount, even if its market value rises to $700,000.
- Adjustments to this book value are typically made only through systematic allocation processes like depreciation (for tangible assets) or amortization (for intangible assets), which are based on the original cost.
- The cost in cash or cash equivalent at the time of purchase is frequently used to compute historical cost.
- It contributes to the consistency and comparability of financial reporting, allowing stakeholders to make informed assessments of an entity’s financial position.
- Similarly, for an intangible asset like a patent with a historical cost of $20,000 and a 5-year life, the annual amortization expense of $4,000 would appear on the income statement.
- For example, a bakery purchasing an oven for $5,000 with $200 in delivery costs records a historical cost of $5,200, which remains consistent on the balance sheet unless depreciated.
Actual cash value means the cost of replacing damaged property with other property of like kind and quality in the physical condition of the property immediately before the damage. Accumulating costs means collecting cost data in an organized manner, such as through a system of accounts. When an asset’s value drops significantly below its book value due to damage, obsolescence, or market changes, you must write it down to reflect the impairment. However, based on IFRS, Building was initially booked at its original cost and then depreciated based on its economic use or at the fair value per the revaluation model. For example, the Office Building of ACB Company was originally purchased for $500,000; ten years later, in 2016, the market value of the building is $1,500,000. In Feb 2015, Infosys bought two companies, ‘Panaya’ and ‘Skava,’ for USD 340 million.
- If the future benefit of a cost cannot be determined, it should be charged to expense immediately.
- The historical cost principle shapes how businesses communicate their financial position to the world.
- GAAP and IFRS permit or require mark-to-market accounting for these assets to ensure financial statements reflect current economic conditions.
- According to the cost principle, transactions should be listed on financial records at historical cost – i.e. the original cash value at the time the asset was purchased – rather than the current market value.
- Similarly, expenses are recognized when they are incurred, even if the payment has not yet been made.




